Human body spine
The human spine, also referred to as the backbone or vertebral column, is vital for our health and well-being. It provides essential support to the body’s framework while safeguarding the spinal cord, which plays a key role in relaying signals between the brain and the rest of the body. Here is a picture of the human spine
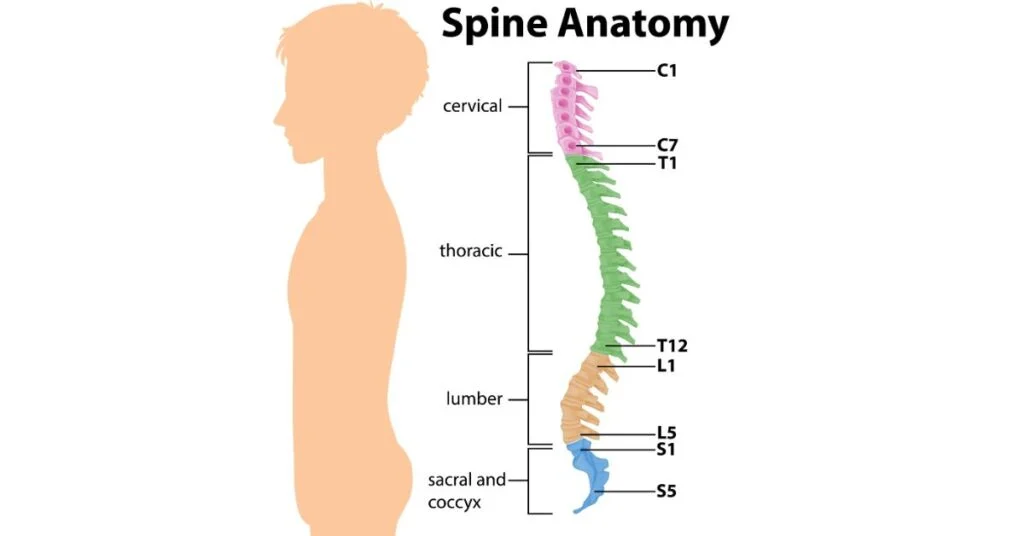
Anatomy of the Spine
The human back consists of 33 bones called vertebrae arranged in a column. These vertebrae are divided into five distinct regions with specific roles and characteristics.
Cervical Spine (neck region)
The cervical backbone, which includes seven vertebrae (C1–C7), forms the neck region. It supports the head and allows for a wide range of motion, including turning, nodding, and tilting.
Thoracic Spine (upper and mid back)
The thoracic back comprises 12 vertebrae (T1-T12), each attached to the ribs.
This region protects vital organs like the heart and lungs.
It is more rigid and less mobile than other sections, providing a stable base for the upper body.
Lumbar Spine (Lower Back)
The lumbar backbone comprises five large vertebrae (L1-L5) that bear the body’s weight. This region is highly mobile and often the source of lower back pain due to its constant stress during movements like bending and lifting.
Sacral Spine (Pelvic Area)
The sacrum has five fused vertebrae.
It forms the back of the pelvis and helps connect the spine to the hips.
The sacrum stabilizes the pelvis and supports the weight of the upper body.
Coccyx (Tailbone)
The coccyx, or tailbone, comprises four fused vertebrae at the very bottom of the spine. Although it has little function, it is an attachment point for muscles and ligaments.
Natural Curves of the Spine
The human back is not a straight column it is a chain of gentle curves
Cervical Lordosis (inward curve in the neck).
Thoracic Kyphosis (outward curve in the mid-back).
Lumbar Lordosis (inward curve in the lower back).
Sacral Kyphosis (outside curve in the pelvic area).
Common Spine Related Issues(rare spinal diseases)
The backbone is vulnerable to numerous conditions and injuries, many of which can result in persistent pain or decreased mobility. Here are some of the most recognized spine-related issues.
Herniated Disc
When the soft inner core of a disc pushes through its outer layer, it can press on surrounding nerves, leading to pain, numbness, or weakness. This condition most commonly occurs in the lumbar region.
Scoliosis
This is a condition where the spine curves abnormally to the side, resulting in a “C” or “S” shape. Scoliosis often develops during adolescence in severe cases can lead to back pain and other health complications.
Spinal Stenosis
Spinal stenosis arises when the spaces within the spine narrow, putting pressure on the vertebral column and nerves. It is often caused by age-related wear and tear and can lead to pain, numbness, and difficulty walking.
Osteoporosis
is a condition that weakens bones, making them more liable to fractures, especially in the vertebrae. It often attacks older adults, especially females, and can result in breaks in the spine, even from slight injuries.
Sciatica
Sciatica is a condition marked by discomfort that travels along the sciatic nerve which stretches from the lower back through the hips and down each leg. This discomfort often results from a herniated disc or bone spur squeezing the nerve.
Kyphosis and Lordosis
These conditions involve abnormal curvatures of the spine. Kyphosis causes an exaggerated forward arching of the upper back, while lordosis leads to excessive inward bending of the lower back.
Electrophysiological Tests for Nerve and Muscle Function
These assessments help assess how efficiently the nerves and muscles surrounding the spine are operating. They are frequently utilized when symptoms such as discomfort, numbness, tingling, or muscle frailty are evident.
Electromyography (EMG)
The purpose of EMG is to measure the electrical activity in muscles to determine whether muscle weakness or pain is caused by nerve damage or muscle dysfunction. A small needle is inserted into the muscles to detect electrical signals.
Use
Helps diagnose conditions like pinched nerves, radiculopathy, or nerve damage from herniated discs.
Nerve Conduction Study (NCS)
Purpose: NCS measures how quickly and efficiently electrical impulses travel through the nerves. This test is often done alongside EMG to assess whether nerve damage affects muscle function.
Use: Commonly used to diagnose conditions like sciatica, carpal tunnel syndrome, or other nerve compression disorders.
Examination and Diagnostic Methods for Spine Health
Diagnosing backbone conditions requires a combination of physical evaluations and advanced diagnostic tools. Here are some modern and precise tests. commonly used by healthcare professionals to assess spinal health and identify underlying issues.
Physical Examination
A physical examination is fundamental and the initial step in identifying spine issues. It includes:
Posture Assessment: Doctors examine the spine for abnormal curves like scoliosis or exaggerated lordosis (swayback).
Mobility Tests: The patient performs movements like bending, twisting, and walking to detect mobility restrictions.
Palpation: Soft pressing on the spine and muscles to identify regions of discomfort and swelling
Neurological Check: Reflexes, muscle strength, and sensory responses are tested to detect nerve involvement.
conclusion
The spine is a complex and vital structure that supports the body, protects the spinal cord, and enables movement. Understanding its anatomy and functions, as well as adopting healthy habits such as good posture, consistent exercise, and weight control can help anyone preserve a healthy back and prevent common problems like back pain or back conditions.
FAQ’s
What is a herniated disc?
A herniated disc occurs when the soft inner nucleus of a spinal disc protrudes through its outer layer, often compressing nearby nerves. This can lead to discomfort, tingling, or weakness, particularly in the lumbar area.
What symptoms are frequently linked to a herniated disc?
Symptoms encompass discomfort, numbness, tingling sensations, and weakness, usually in the lower back, legs, or arms, depending on the site of the herniation.
How are kyphosis and lordosis different?
Kyphosis involves an outward rounding of the upper back, while lordosis is an excessive inward curvature of the lower back.
How can I maintain a healthy spine?
To maintain spine health, practice good posture, exercise regularly, lift properly, stay hydrated, and avoid prolonged sitting. Incorporating ergonomic practices into your daily routine is also beneficial.
What is the total number of l discs in the human body?
The human body contains 23 intervertebral discs.
6 discs in the cervical (C)
12 discs in the thoracic (T)
5 discs in the lumbar (L)
Which region is most commonly affected by an IVDP?
The lumbar region is the most common site for intervertebral disc protrusion, as it bears a significant portion of the body’s weight and is crucial for various movements.